Established efficacy
in focal seizures1
living with focal seizures.
Pivotal trial results
The established efficacy of BRIVIACT provides a strong treatment foundation
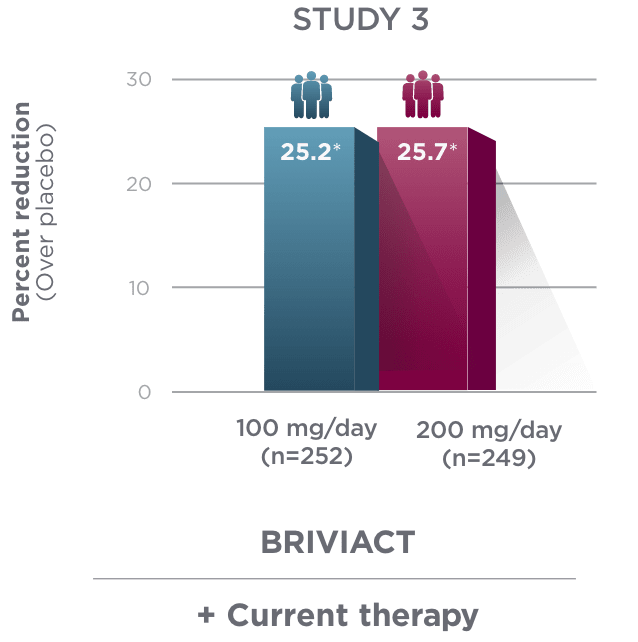
Percent reduction (BRIVIACT adjunctive therapy over placebo) in focal
seizure frequency adjusted to 28 days during the treatment period1
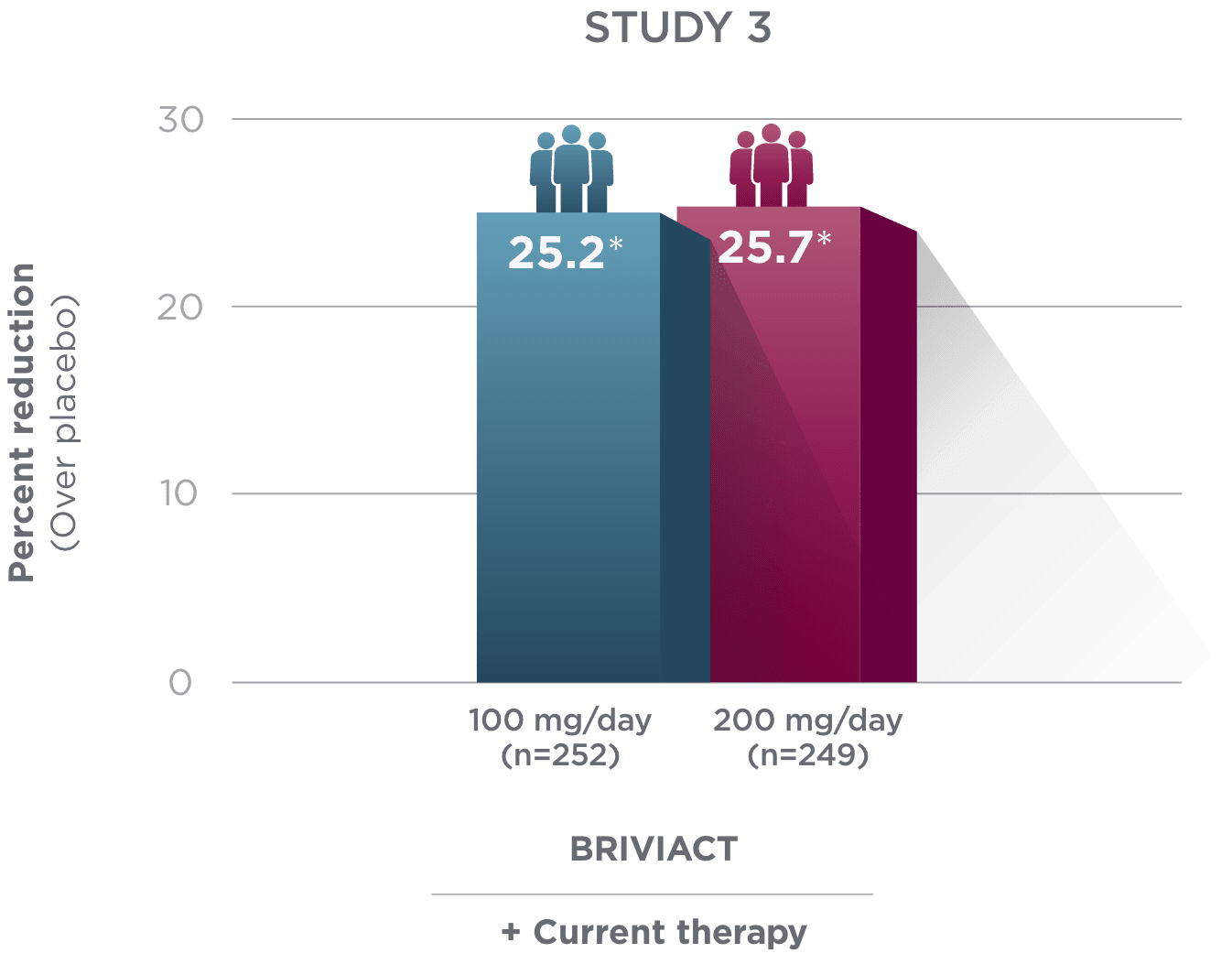
*
Statistically significant based on testing procedure with alpha=0.05.1
Across all 3 trials, low discontinuation rates
due to adverse events were observed1:
- Placebo: 4%
- BRIVIACT 50 mg/day: 5%
- BRIVIACT 100 mg/day: 8%
- BRIVIACT 200 mg/day: 7%
- Effectiveness was established in 3 fixed-dose, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter studies with a 12-week treatment period, and comprised 1,550 adult patients
- Enrolled adult patients had focal seizures that were not adequately controlled by 1 to 2 concomitant ASMs
- Patients taking concomitant levetiracetam were excluded from Study 3
ASM=antiseizure medication.
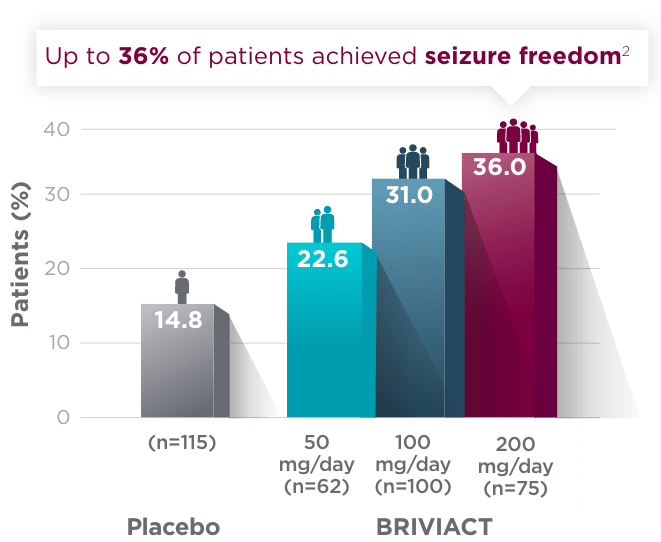
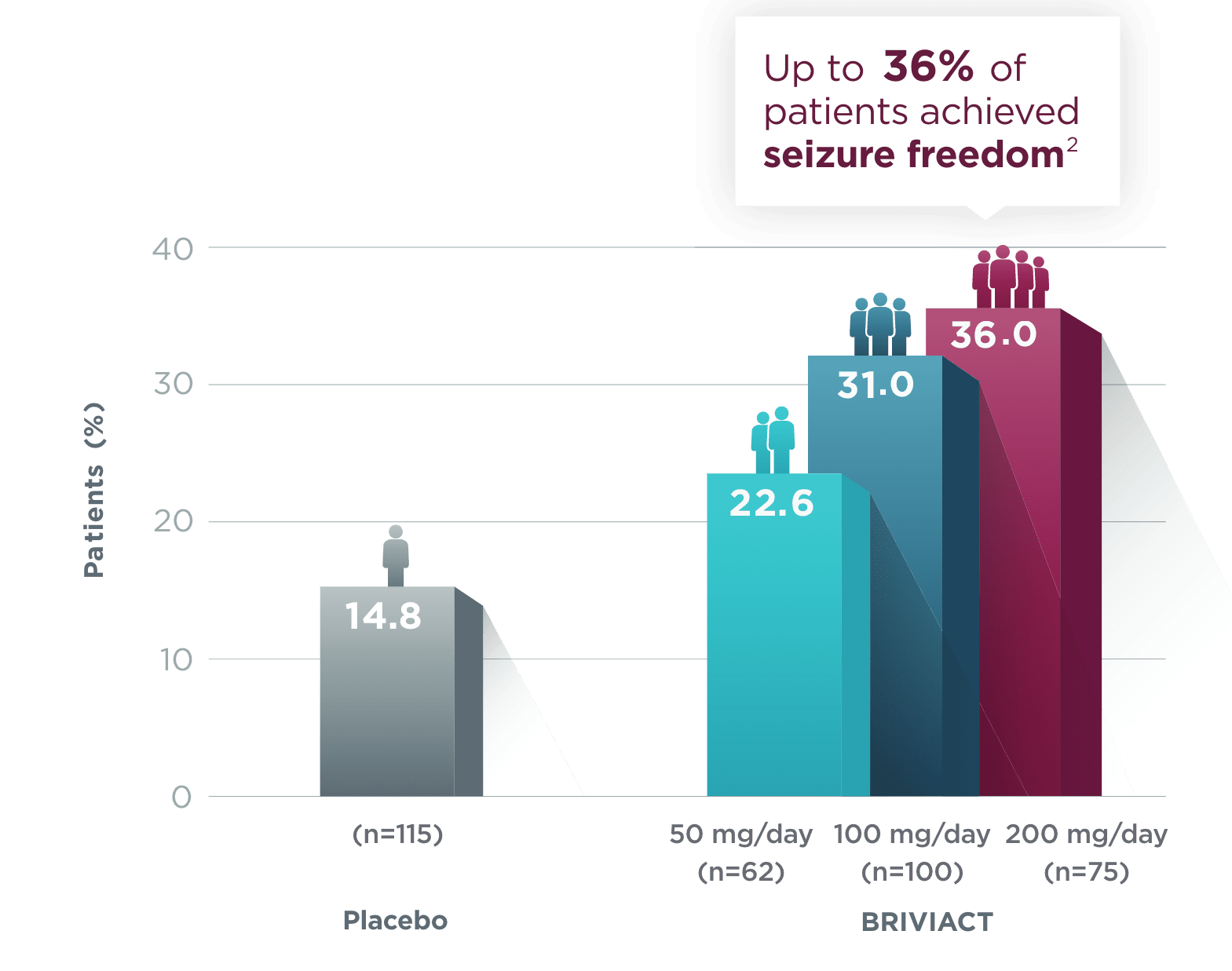
SGTC seizure freedom
From a baseline of ~3 SGTC seizures per 28 days,
More than 1 in 3 patients achieved zero SGTC seizures in both the short and long term2,3
Short-term (12-week) SGTC seizure freedom rate from a pooled
post hoc analysis2
Long term (5 years)
More than 1 in 3 patients overall (35%) experienced
zero SGTC seizures for at least one year during the
long-term follow-up post hoc analysis3
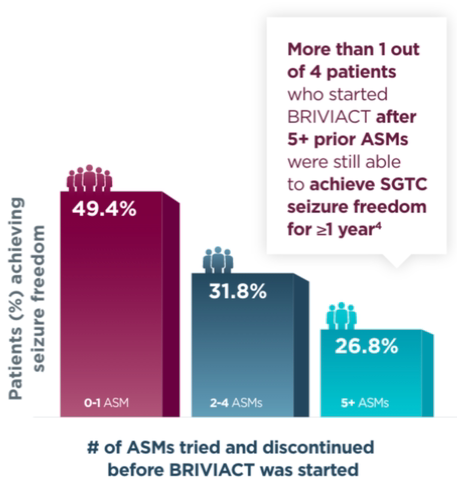
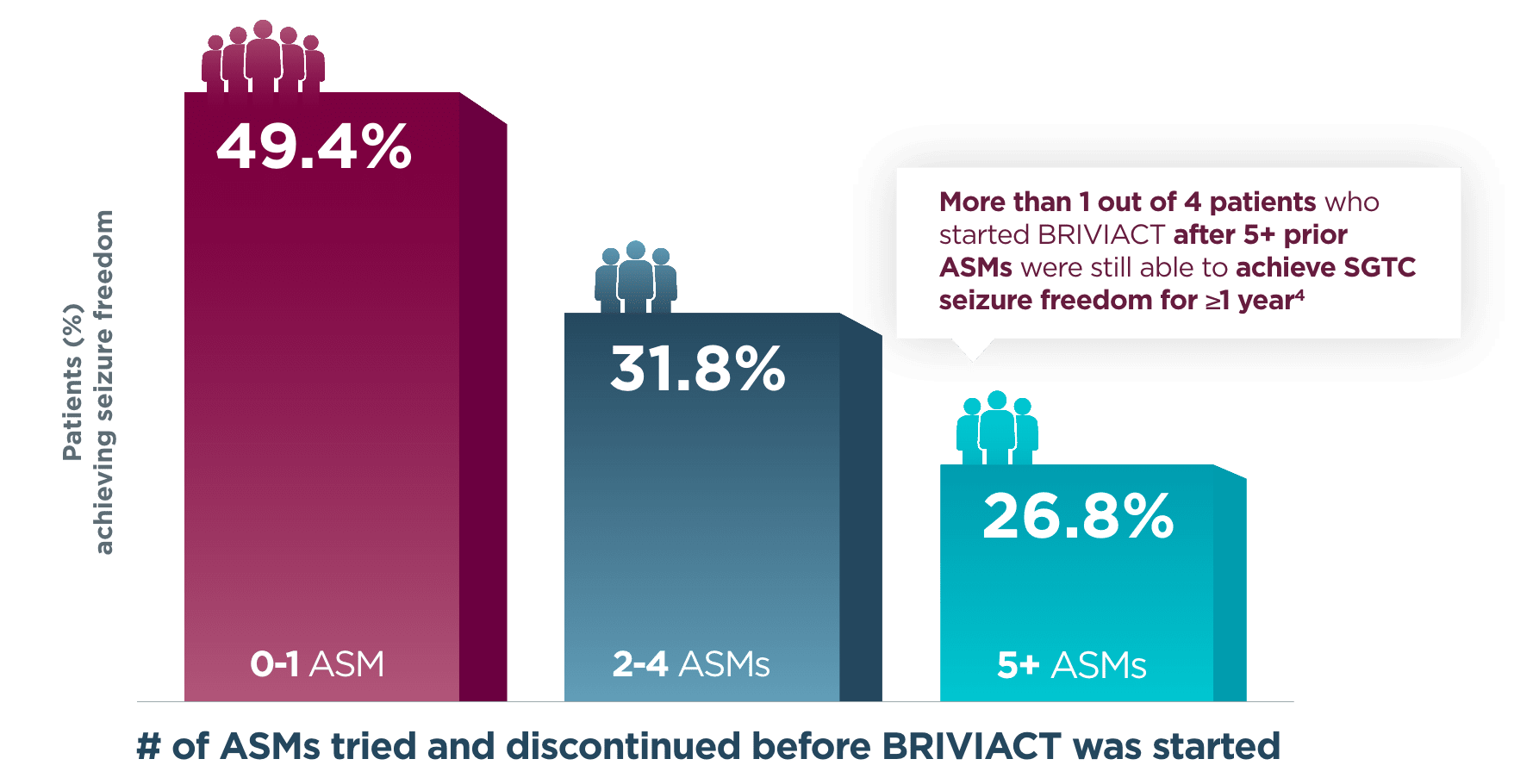
Approximately half of patients achieved seizure freedom for a year or more when BRIVIACT was used earlier in the treatment regimen4
Patients with ≥1 year SGTC seizure freedom at any time during the long-term
(5-year) follow-up post hoc analysis4
Patients received adjunctive BRIVIACT in either the pivotal trials or the long-term follow-up3
More patients achieved zero SGTC seizures
when BRIVIACT was started earlier4
- 12 weeks: Post hoc analysis of patients with SGTC seizures among their baseline seizures from pooled data of three Phase 3 pivotal trials2
- 5 years: Post hoc analysis conducted to evaluate the efficacy and tolerability of long-term BRIVIACT treatment in patients ≥16 years of age, who reported SGTC seizures during the 8-week baseline of three Phase 3 pivotal trials and received adjunctive BRIVIACT in either the pivotal trials or the long-term follow-up3
- Efficacy (concomitant levetiracetam excluded) and tolerability (concomitant levetiracetam included) were assessed from the first day of BRIVIACT in patients who initiated BRIVIACT at 50-200 mg/day3
BRIVIACT was studied in a difficult-to-treat patient population, including refractory patients who had taken 5 or more ASMs (34%)3
SGTC=secondarily generalized tonic-clonic.
References: 1. BRIVIACT® (brivaracetam) prescribing information. Smyrna, GA: UCB, Inc. 2. Moseley BD, Sperling MR, Asadi-Pooya AA, et al. Efficacy, safety, and tolerability of adjunctive brivaracetam for secondarily generalized tonic-clonic seizures: pooled results from three phase III studies. Epilepsy Res. 2016;127:179-185. doi:10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2016.09.003 3. Moseley BD, Dimova S, Elmoufti S, Laloyaux C, Asadi-Pooya AA. Long-term efficacy and tolerability of adjunctive brivaracetam in adults with focal to bilateral tonic-clonic (secondary generalized) seizures: post hoc pooled analysis. Epilepsy Res. 2021;176:106694. doi:10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2021.106694 4. Moseley BD, Dimova S, Elmoufti S, Laloyaux C, Asadi-Pooya AA. Long-term efficacy and tolerability of adjunctive brivaracetam in adults with focal to bilateral tonic-clonic (secondary-generalized) seizures: post hoc pooled analysis. Epilepsy Res. Journal Pre-proof, 2021.