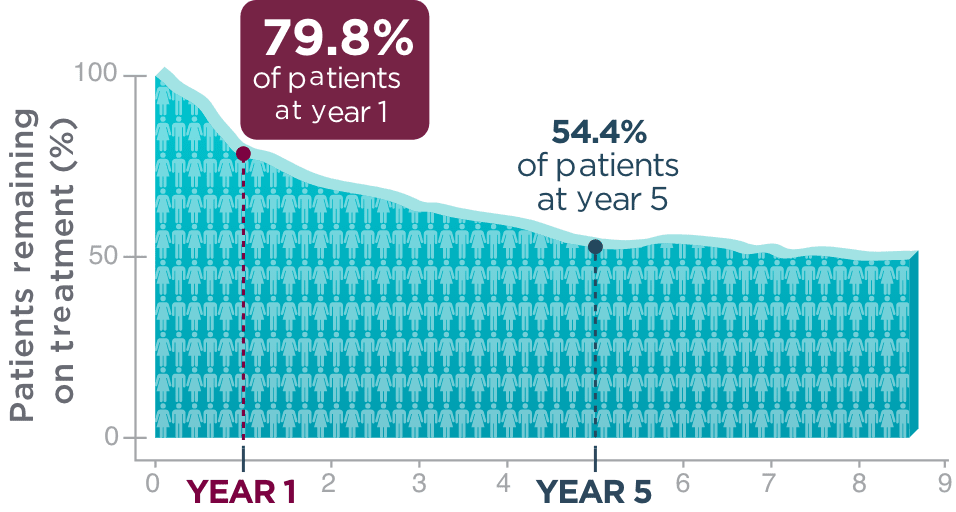
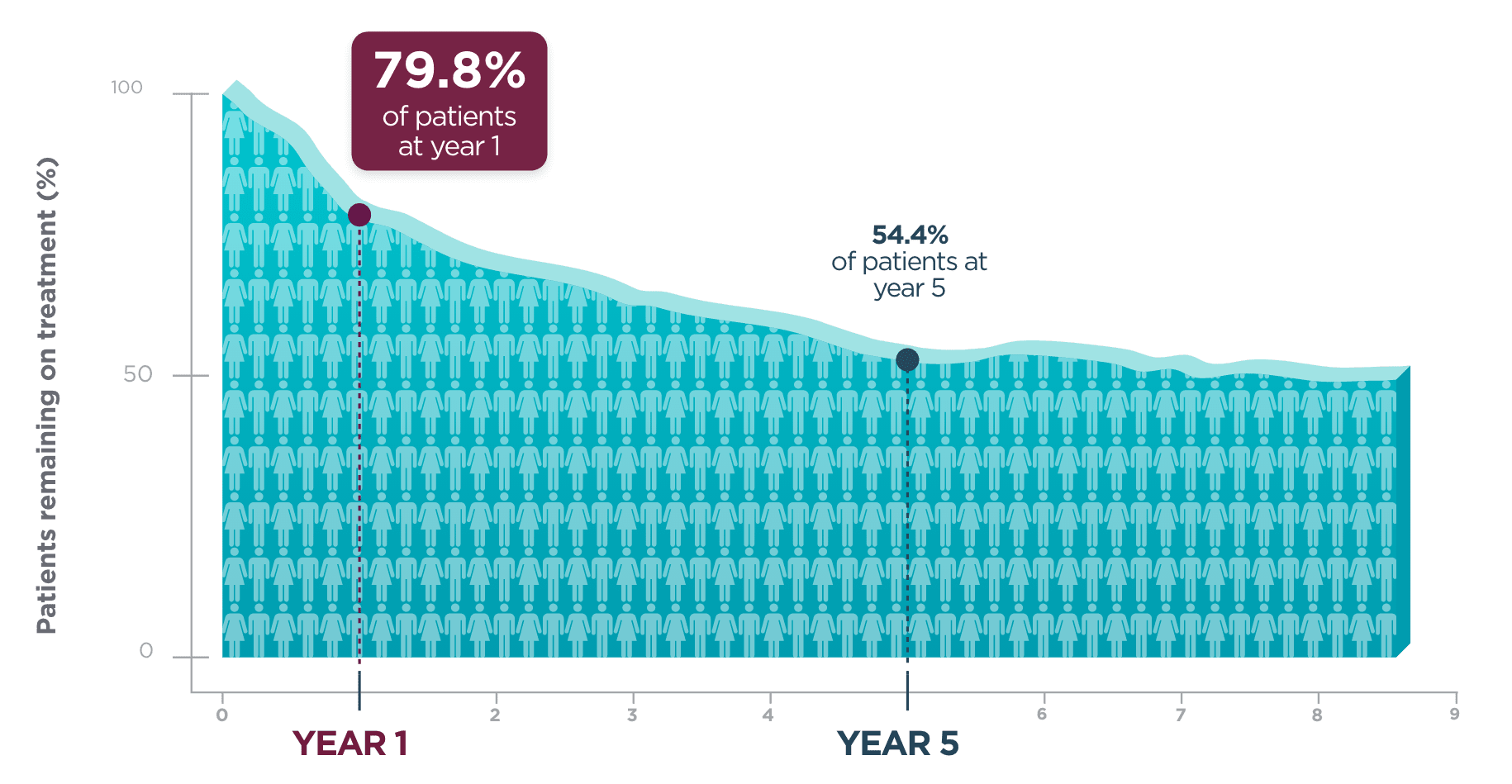
Long-term retention
in adult patients
living with focal seizures.
One year after beginning BRIVIACT, ~8 out of 10 patients
were still on treatment1
Kaplan-Meier curve of adult patients remaining on treatment
in a pooled
study1
Adapted from Toledo et al, 2016.
Five years post-initiation, more than half of patients were still taking BRIVIACT1
About the analysis:
-
The analysis was focused on time to discontinuation among patients uncontrolled by 1-3 ASMs1
- Patients who discontinued due to a lack of efficacy and adverse events were included1
- Patients who discontinued for other reasons were censored1
- These retention data are based on Kaplan-Meier analyses of how long patients remained on BRIVIACT. Conclusions of long-term efficacy or safety should not be drawn based on this data
- Limited exposure was seen at the later time points; 41 patients (1.7%) continued treatment for ≥8 years, and 3 patients (0.1%) continued for ≥8.5 years1
- Adult patients with epilepsy from Phase 2b and Phase 3 trials, uncontrolled by 1-3 ASMs
- Patients continued into an open-label, long-term (5-year analysis), follow-up trial, taking BRIVIACT 50-200 mg/day (N=2,051)
ASM=antiseizure medication.
Reference: 1. Toledo M, Whitesides J, Schiemann J, et al. Safety, tolerability, and seizure control during long-term treatment with adjunctive brivaracetam for partial-onset seizures. Epilepsia. 2016;57(7):1139-1151. doi:10.1111/epi.13416