A strong treatment
foundation with BRIVIACT1
Pivotal trial results
BRIVIACT efficacy extrapolated for pediatric patients
Effectiveness determined through extrapolation from adult efficacy data to children 1 month and older1
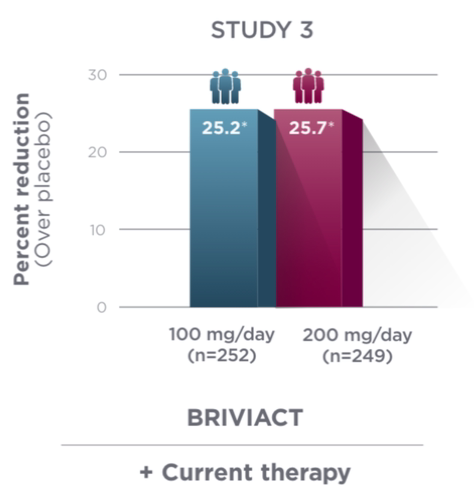
Percent reduction (BRIVIACT adjunctive therapy over placebo) in focal
seizure frequency adjusted to 28 days during the treatment period1
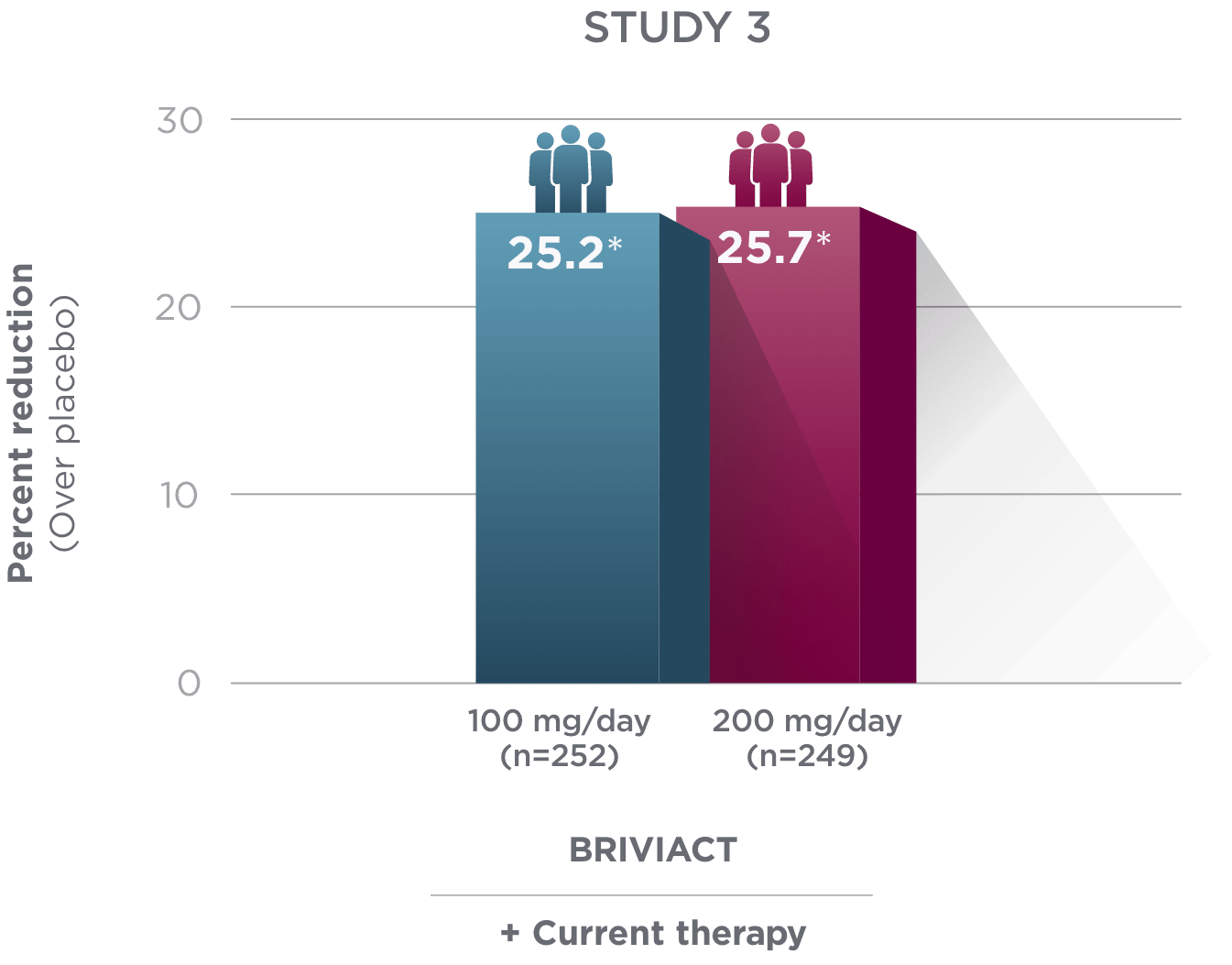
*
Statistically significant based on testing procedure with alpha=0.05.1
- Effectiveness was established in 3 fixed-dose, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter studies with a 12-week treatment period, and comprised 1,550 adult patients
- Enrolled adult patients had focal seizures that were not adequately controlled by 1 to 2 concomitant ASMs
- Patients taking concomitant levetiracetam were excluded from Study 3
ASM=antiseizure medication.
Population data
BRIVIACT efficacy was studied in a challenging pediatric population2
The majority of these patients (58%) had taken at least 2 prior ASMs and were all on concomitant ASMs2
Pediatric trial results2

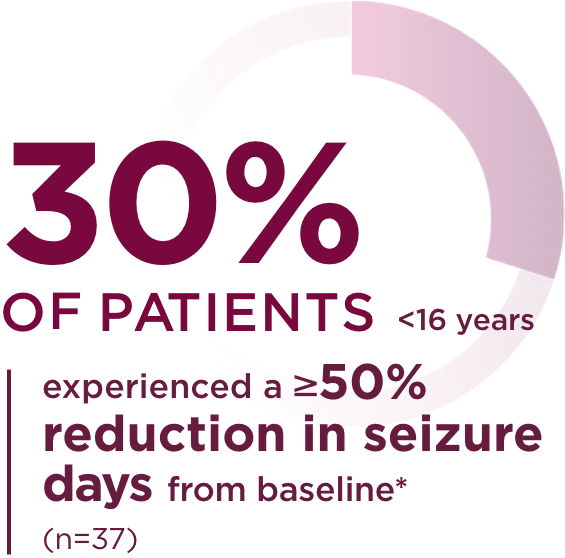
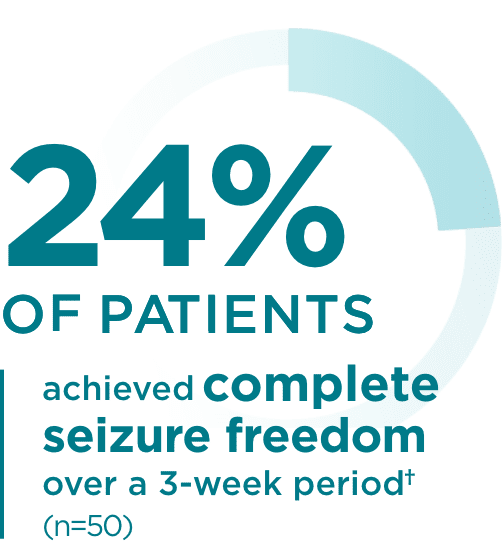
*Patients without seizures in baseline were excluded. Number of seizure days
standardized to a 28-day duration.2
†With or without secondary generalization and no primary generalized seizures at baseline.2
- Phase 2a, open-label, single-arm, fixed 3-step dose-escalation trial
- Short-term safety and tolerability, pharmacokinetics, preliminary efficacy of BRIVIACT oral solution. Efficacy analyses were exploratory
- Pediatric patients 1 month to <16 years of age
- 1-week baseline period, 3-week evaluation period
- In the treatment period, BRIVIACT oral solution dosage was divided into 2 daily doses and increased each week to approximately 0.8, 1.6, and 3.2 mg/kg/day for patients aged ≥8 years, and 1.0, 2.0, and 4.0 mg/kg/day for patients aged <8 years
- 99 patients were enrolled in the trial. 52 patients with focal seizures were included in the safety analysis, and 50 were included in the efficacy analysis. Only those patients experiencing seizures in the 1-week baseline period (n=37) were included in the seizure reduction and responder rate analyses. All 50 patients with focal seizures were included in the seizure freedom analysis
References: 1. BRIVIACT® (brivaracetam): prescribing information. Smyrna, GA: UCB, Inc. 2. Liu E, Dilley D, McDonough B, Stockis A, Daniels T. Safety and tolerability of adjunctive brivaracetam in pediatric patients <16 years with epilepsy: an open-label trial. Paediatr Drugs. 2019;21(4):291-301. doi:10.1007/s40272-019-00332-y